THYMOQUIN INTRODUCTION
One of the most revered traditional herbal remedies is the oil from black seed or cumin (Nigella sativum). In fact, black seed is mentioned more frequently than any other plant in the Bible. Native to the Middle East, India, North Africa, Mediterranean, and western Europe, black seed has been used as a food and medicine for over 2,500 years. Some ancient texts referred to black seed oil as a “panacea for all ailments except for mortality.”1
This wonderful gift from nature is being rediscovered via intense scientific investigations as a health aid to address some of the major health issues of modern times. Mainly obesity, insulin resistance, cardiovascular health, joint health, and chronic inflammation. The emerging data is extremely positive, yet underappreciated.1-6
While black seed oil (BSO) preparations are gaining popularity in the marketplace, based upon the results from human clinical trials along with its historical place, it is easy to judge that BSO is not as popular as it should be.
Why Full-Spectrum Standardization Matters
BSO is packed full of active compounds. Most of the research focus is on a key compound, thymoquinone.7,8 But other compounds are that are important to the overall actions of BSO. These other ingredients include various volatile compounds known as terpenes and terpenoids, as well as sterols and saponins, polyphenols, and other antioxidant phytochemicals. Critical to insuring a balanced and full-spectrum BSO is using freshly harvested black cumin seeds that are then cold-pressed versus extracted for higher thymoquinone content.
Figure 1. Black Seed Oil’s Full Spectrum of Phytochemical Compounds
ThymoQuin® is the premier cold-pressed BSO produced from a freshly harvested, non-GMO cumin variety naturally bred to yield a higher thymoquinone content. ThymoQuin® provides a standardized, full-spectrum BSO with optimal ratios of all the bioactive compounds found in black seeds in a very precise ratio for ultimate synergistic effect. ThymoQuin® is patented (US Patent #11,883,455) and is the only BSO that meets the USP monograph.
ThymoQuin® is standardized to contain 3% thymoquinone combined with other important bioactives at optimal levels including a less than 2% concentration of free fatty acids (FFAs). ThymoQuin® contains a sunflower proprietary blend (SPB) of compounds that produce a considerable increase in bioavailability (see orange line versus the green line in the Figure 2 below).
Figure 2. Bioavailability of Thymoquinone in Mice is Enhanced in ThymoQuin®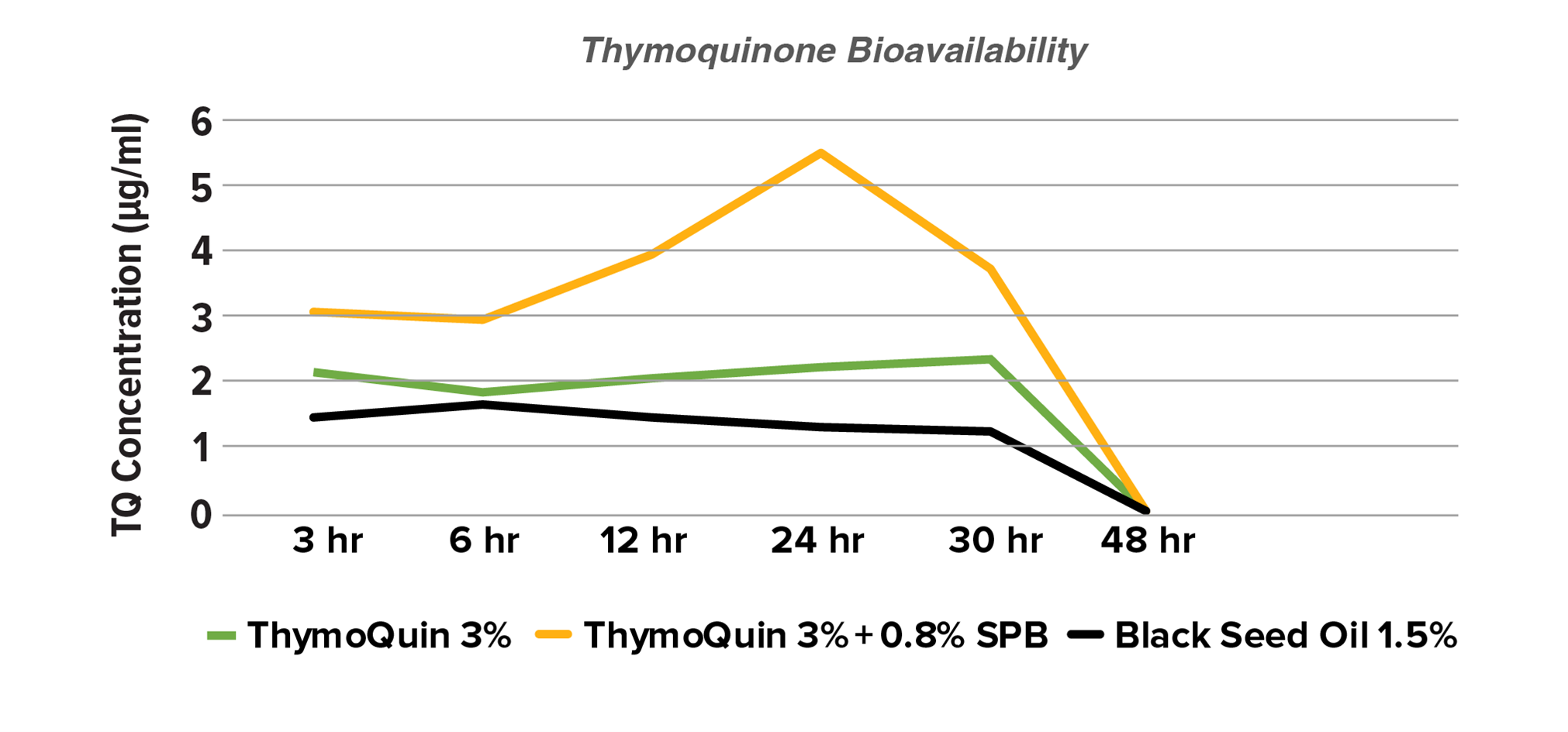


Health Benefits of Black Seed Oil
Significant preclinical and human clinical studies have shown BSO to produce positive effects on supporting blood sugar control, blood pressure, heart rate, mood, and inflammation as well as showing antistress and immune-enhancing effects in athletes. The mechanisms underlying these health benefits are related to seven major actions, particularly in cardiometabolic disorders such as obesity, metabolic syndrome, and various cardiovascular issues:
- Enhances antioxidant activity. BSO components not only exert direct antioxidant effect, but they also increase the body’s own protective mechanisms against oxidative damage. Foremost in this regard is the increase in the activity of the body’s antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione reductase. The antioxidant effects provide benefit to all body systems, including immune function and the brain.1,6
- Enhances anti-inflammatory activity. Chronic inflammation is a big underlying factor in aging and the development of chronic health issues like heart disease. BSO exerts an action in inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway that leads to the formation of pro-inflammatory compounds known as cytokines.1,6
- Enhances mitochondrial function. In addition to the antioxidant protection offered to mitochondria, thymoquinoine upregulate the expression of proteins that are key activators of mitochondrial energy production.10
- Enhances the health of the microbiome. In addition to inhibiting the growth of undesirable microbes, BSO promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms.11
- Enhances insulin sensitivity. The development of resistance to insulin is a key factor in the development of obesity. BSO enhances insulin sensitivity via several mechanisms including enhancing GLP-1 secretion and activating a key enzyme known as AMP-kinase.12,13
- Enhances cholesterol metabolism. BSO components help to improve cholesterol metabolism by activating AMPk and increasing the expression of receptors for LDL cholesterol on liver cells. Both actions provide feedback to the liver cell that reduces cholesterol manufacture.5,14
- Enhances blood flow. BSO components increase the utilization of nitric oxide, a compound produced by cells that line blood vessels. Nitric oxide leads to better blood flow and improved blood pressure control.15
Because of these seven key mechanisms there are widespread health applications of BSO. It can literally support and improve health in virtually anyone taking it. However, the focus of most of the recent research of BSO in humans has been in evaluating its support of cardiometabolic health and, in particular, obesity.1-6
Black Seed Oil Reduces Obesity and Diabetes Associated Oxidative Stress
Obesity is often a key source of stress to metabolic health that carries with it an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Basically, obesity impacts health exactly opposite that of BSO. While BSO produces positive effects on the mechanisms that support health, obesity produces negative effects.
For example, obesity is often characterized by oxidative stress, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Fortunately, even in obese individuals, BSO counteracts this negative stress.4 This benefit was shown quite clearly in double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in obese women given BSO supplementation. These women were between the ages of 25 to 50 years old with body mass index (BMI) between 30-35 (basically indicating they were more than 40 pounds above their ideal body weight.
In one study, obese women were randomly assigned to receive BSO (3 grams daily) or a placebo, along with a low-calorie diet for eight weeks.16 The BSO produced significant decreases in weight and waist circumference measurements compared with the placebo group. The BSO supplemented group also showed a significant increase in a key antioxidant enzyme (superoxide dismutase) and significant reductions in biomarkers of inflammation. One inflammatory marker familiar to many is C-reactive protein (CRP), a well-known risk factor of cardiovascular disease. CRP was reduced by 54.5% in the BSO group versus 21.4% in the placebo group.
Clinical Studies with Black Seed Preparations
Various forms of black seed have been utilized in human double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies including preparations of crude seed powder, extracts, and various concentrations of BSO at random dosage levels. This variation of form, quality, and dosage levels makes it difficult for clear evaluation of benefits of BSO. The standardization offered by ThymoQuin® represents a big step for producing consistent results and clinical evaluation of the health benefits of black seed preparation.
Thymoquin is more concentrated than the black seed preparations used of in the published clinical research and is also much better absorbed and utilized. Hence, the recommended dosage is 500 to 1,000 mg daily.
In addition to the studies discussed above, there are several other studies that are important to call out. First, over 20 human clinical trials have substantiated the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits of BSO in a variety of test subjects.1,6 And this includes studies in subjects experiencing severe inflammation. For example, three clinical studies have evaluated the effects of BSO (500 mg twice daily) in subjects with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), one of the most severe inflammatory conditions in humans.17 The results from these studies showed significant reductions in several markers of inflammation and oxidative stress after 8 weeks of supplementation compared to baseline measurements. These results and others support the use of BSO as a general nutritional support for inflammation.
BSO is also a great “brain food” as all seven of its mechanisms action are particularly beneficial for brain health. Two double-blind human clinical studies highlight this potential benefit. In one study in healthy males over 50 years of age, those given 500 mg of black seed powder for 9 weeks showed significant improvements in memory, attention, and mental function.18 And in another study with the same dosage for four weeks, the black seed powder showed an improvement in mood and feelings of anxiousness along with improved mental function in a study of 48 healthy adolescent males between the ages of 14 to 17 years old.19 These results indicate that ThymoQuin® may have positive effects of mood, memory, and brain function at any age.
And let’s not forget one of black seed’s major traditional use as a digestive aid. In both the Ayurvedic and Unani systems of medicine it was used primarily for its benefits in abdominal bloating, gas, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal issues. These effects are now known to be due to both its volatile compounds and thymoquinone as well as through its modulating effects in promoting an improved microbiome.20
Human Clinical Studies with ThymoQuin®
ThymoQuin® has its own scientific portfolio of preclinical and human clinical studies highlighting its positive effects on supporting a variety of health goals.
The first double-blind, placebo-controlled study with ThymoQuin® was published in 2020. It was conducted on twenty healthy adults (average age 55 years old, average BMI 29.6). The study was designed to look at the effects of ThymoQuin® supplementation for six weeks on vascular function (i.e., blood pressure measurements) compared to a placebo. At baseline, the mean blood pressure was 143.5/90.7 mm Hg. Following the six-week supplementation it was 127.3/79.6 mm Hg. This represented a significant improvement in vascular health.21
Two other human clinical trials have been published on the effects of ThymoQuin® in marathon runners. This group represents a good test on the effects of ThymoQuin® in combating stress and promoting recovery. Marathon runners are more susceptible to upper respiratory tract infections and the mental effects of stress the three weeks prior to and one week after an event. In the first study, 37 runners (13.1-mile half-marathon and 26.2-mile marathon distance) consumed 500 mg of ThymoQuin® or placebo daily three weeks before and one week following a marathon or half-marathon competition.22 Compared to placebo, subjects in the ThymoQuin® supplementation group reported significantly fewer upper-respiratory tract symptoms such as such as cough, sore throat, sinus congestion, etc., and better overall well-being (e.g. lower stress, increased energy), as well as lower cortisol levels, and greater intestinal microbiome diversity. These results show that ThymoQuin® black can improve immune system function and overall well-being following the stress of intense endurance training and competition. It also suggests that some of these may be the result of an improved intestinal microbiome. through the Gut-Immune-Axis.
In the other other study in marathon runners, ThymoQuin® (500 mg) was combined with an omega-3 fatty acid-rich fish oil (1,500 mg).23 The runners consumed either the supplement or a placebo daily three weeks before and one week following a marathon or half-marathon competition. In both studies, the runners in the supplementation group reported the same benefits as the first study: significantly fewer upper-respiratory tract symptoms and better overall well-being, as well as lower cortisol and superior microbiome composition.
Synergistic Effects
In addition to potentiating the effects of fish oils, ThymoQuin® has also been shown to potentiate the health benefits of other natural products including astaxanthin, beta-carotene, lutein, Pycnogenol®, and vitamin D.24 Here are some of the synergistic increases seen in cell culture models of inflammation:
- Astaxanthin with ThymoQuin® – 2X increased anti-inflammatory effect
- Lutein with ThymoQuin® – 3.3X times increased anti-inflammatory
- Pycnogenol® with ThymoQuin® – 21X times increased anti-inflammatory effect
- Vitamin D with ThymoQuin® – 6X increased anti-inflammatory effect
These results indicate ThymoQuin® is a synergistic potentiator of other health promoting compounds. Often dietary factors work in harmony to produce a total effect or force that is greater than the sum of the individual factors. In other words, it is a situation whereby 1+1+1 does not equal 3, but something much greater. However, ThymoQuin®’s synergistic effects appear to be extremely far reaching. This action is provocative. Perhaps the greatest benefit of ThymoQuin® is not its own pharmacology, but rather its ability to amplify all of the health promoting properties of all of the myriads of beneficial components that we consume in food and as dietary supplements. Regardless, it is truly one of the greatest gifts in Nature’s pharmacy.
References
- Wahab S, Alsayari A. Potential Pharmacological Applications of NigellaSeeds with a Focus on Nigella sativaand Its Constituents against Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: Progress and Future Opportunities. Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 11;12(22):3829.
- Ferizi R, Ramadan MF, Maxhuni Q. Black Seeds (Nigella sativa) Medical Application and Pharmaceutical Perspectives. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2023 Apr-Jun;15(2):63-67.
- Al Asoom L. Is Nigella sativaan Effective Bodyweight Lowering Agent and a Mitigator of Obesity Risk? A Literature Review. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2022 Jul 12;18:495-505.
- Adam SH, Abu IF, Kamal DAM, Febriza A, Kashim MIAM, Mokhtar MH. A Review of the Potential Health Benefits of Nigella sativaon Obesity and Its Associated Complications. Plants (Basel). 2023 Sep 8;12(18):3210.
- Shabani M, Ghavidel F, Rajabian A, Homayouni-Tabrizi M, Jamialahmadi T, Hosseini H, Sahebkar A. Effect of Nigella sativa Consumption on Lipid Profile and Glycemic Index in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Curr Med Chem. 2024 Jan 23.
- Kavyani Z, Musazadeh V, Golpour-Hamedani S, Moridpour AH, Vajdi M, Askari G. The effect of Nigella sativa (black seed) on biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Jun;31(3):1149-1165.
- Aslani MR, Saadat S, Boskabady MH. Comprehensive and updated review on anti-oxidant effects of Nigella sativaand its constituent, thymoquinone, in various disorders. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(8):923-951.
- Sadeghi E, Imenshahidi M, Hosseinzadeh H. Molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its active constituent, thymoquinone: a review. Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jun;50(6):5439-5454.
- Yeun K, Akshay A, Rafaelle M, et al. Beneficial efect of 3% thymoquinone on stem-cell-mediated improvement in immune system and anti-inflammatory function. J Food Nutr Sci. 2021;3(3) 63-74.
- Isaev NK, Chetverikov NS, Stelmashook EV, Genrikhs EE, Khaspekov LG, Illarioshkin SN. Thymoquinone as a Potential Neuroprotector in Acute and Chronic Forms of Cerebral Pathology. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2020 Feb;85(2):167-176.
- Akinrinde AS, Adekanmbi AO, Olojo FO. Nigella sativaoil protects against cadmium-induced intestinal toxicity via promotion of anti-inflammatory mechanisms, mucin expression and microbiota integrity. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2022 May-Jun;12(3):241-256.
- Ogen-Shtern N, Margarita Y, von Oppen-Bezalel L. Antimicrobial activity by a unique composition of cold pressed Nigella sativa seed (Black Cumin) Oil. Food Sci Nutr Res. 2021; 4(2): 1-9.
- Shaukat A, Zaidi A, Anwar H, Kizilbash N. Mechanism of the antidiabetic action of Nigella sativaand Thymoquinone: a review. Front Nutr. 2023 Sep 25;10:1126272.
- Sahebkar A, Beccuti G, Simental-Mendía LE, Nobili V, Bo S. Nigella sativa (black seed) effects on plasma lipid concentrations in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Pharmacol Res. 2016 Apr;106:37-50.
- Jaarin K, Foong WD, Yeoh MH, Kamarul ZY, et al. Mechanisms of the antihypertensive effects of Nigella sativa oil in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2015 Nov;70(11):751-7.
- Mahdavi R, Namazi N, Alizadeh M, Farajnia S. Nigella sativa oil with a calorie-restricted diet can improve biomarkers of systemic inflammation in obese women: A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Clin Lipidol. 2016 Sep-Oct;10(5):1203-11.
- Hadi V, Pahlavani N, Malekahmadi M, Nattagh-Eshtivani E, et al. Nigella sativain controlling Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular, and rheumatoid arthritis diseases: Molecular aspects. J Res Med Sci. 2021 Mar 31;26:20.
- Bin Sayeed MS, Asaduzzaman M, Morshed H, et al. The effect of Nigella sativa Linn. seed on memory, attention and cognition in healthy human volunteers. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jul 30;148(3):780-6.
- Bin Sayeed MS, Shams T, Fahim Hossain S, et al. Nigella sativa L. seeds modulate mood, anxiety and cognition in healthy adolescent males. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Feb 27;152(1):156-62.
- Jarmakiewicz-Czaja S, Zielińska M, Helma K, et al. Effect of Nigella sativaon Selected Gastrointestinal Diseases. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Apr 3;45(4):3016-3034.
- Bush B, Pena T, Bush R, et al. Effects of Standardized Black Seed Oil Cold Press Supplement Over A Six Week Period on Blood Pressure and Heart Rate in Healthy Patients: A Nonrandomized Clinical Trial. Food Science & Nutrition Research 2020;3:1-5.
- Talbott SM, Talbott JA. Effect of ThymoQuin Black Cumin Seed Oil as a Natural Immune Modulator of Upper-Respiratory Tract Complaints and Psychological Mood State. Food Sci Nutr Res. 2022; 5(1): 1-6.
- Talbott SM, Talbott JA. Black Cumin seed oil plus fish oil combination modulates gut-immune-axis. EC Nutrition. 2022;17(7):18-27.
- Unpublished Research by TriNutra on ThymoQuin Synergies. 2018. Pharmaseed, Nes Ziona Israel.
